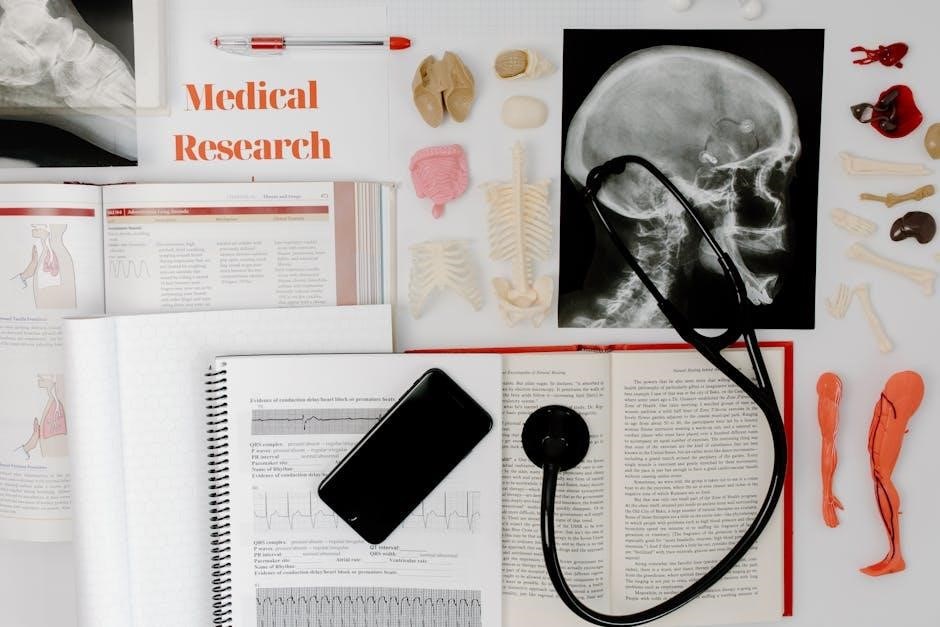
This lab manual provides a comprehensive, hands-on approach to exploring human anatomy and physiology, offering interactive exercises, dissections, and activities to enhance understanding of bodily structures and functions.
1.1 Overview of the Lab Manual
This lab manual is designed for students in human anatomy and physiology courses, offering a structured approach to understanding the human body. It includes pre- and post-lab questions, dissections, and interactive exercises to engage students. The manual covers major body systems, with activities like labeling anatomical models and histological examinations. It also features detailed instructions for cat and fetal pig dissections, providing hands-on experience. The content is tailored for healthcare and science students, emphasizing practical learning and memorization of key terms and structures.
1.2 Importance of Anatomy and Physiology
Understanding anatomy and physiology is foundational for healthcare careers, providing insights into how the body functions. It aids in disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. This knowledge enhances appreciation for the human body’s complexity and promotes informed health decisions. Studying these fields fosters critical thinking and scientific literacy, essential for advancing medical research and practice.
Safety Guidelines and Lab Etiquette
Adhering to safety protocols and proper lab etiquette ensures a secure and respectful environment. This includes wearing protective gear, handling equipment carefully, and maintaining cleanliness to prevent accidents and contamination.
2.1 General Safety Precautions
Ensuring a safe laboratory environment is crucial for all participants. Students must wear protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats when handling biological specimens or chemicals. Proper storage and handling of equipment are essential to prevent accidents. Additionally, maintaining a clean workspace and following disposal protocols for biological materials are vital. Awareness of potential allergies or sensitivities among students is also important. By adhering to these guidelines, the lab environment remains secure and conducive to learning.
2.2 Proper Use of Lab Equipment
Proper use of lab equipment is essential for accurate results and safety. Students should familiarize themselves with tools like microscopes, dissecting instruments, and measurement devices. Always calibrate equipment before use and handle fragile items with care. Follow specific protocols for each instrument to avoid damage or injury. Regularly clean and store equipment to maintain functionality. Misuse can lead to inaccurate data or equipment damage. Refer to the lab manual or instructor for guidance on proper techniques and safety precautions.
Adhering to these practices ensures efficient and effective lab work.
Histology and Microscopy
Histology involves the study of tissue structure under a microscope, while microscopy provides detailed views of cellular arrangements. These techniques are essential for understanding tissue functions and structures.
Histology is the study of tissue structure, essential for understanding how cells organize into functional units. This section introduces students to the four primary tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Through microscopy, students examine tissue samples to identify key features and understand their roles in the body. The lab manual provides activities such as labeling, matching, and written exercises to reinforce learning. Hands-on exploration of histological slides helps students connect microscopic structures to their physiological functions, laying a foundation for advanced anatomical studies.
3.2 Microscopy Techniques
Mastering microscopy is essential for examining cellular structures in histology. This section teaches students to prepare slides, focus specimens, and identify key features under a microscope. Techniques include adjusting magnification, using stains for contrast, and distinguishing between tissue types. The lab manual provides step-by-step guides and exercises to enhance observational skills. By practicing with histological samples, students gain proficiency in identifying microscopic structures, which is crucial for understanding tissue functions and their role in human anatomy and physiology.

Integumentary System
The integumentary system, comprising skin, nails, hair, and associated glands, protects the body, regulates temperature, and aids in sensory perception, playing a vital role in overall health.
4.1 Structure and Function
The integumentary system, comprising skin, nails, hair, and associated glands, serves as the body’s protective barrier. The skin, its largest organ, consists of the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. It regulates body temperature, prevents water loss, and shields against external damage. Hair and nails provide additional protection, while sebaceous and sweat glands maintain skin health and aid in thermoregulation. This system also facilitates sensory perception through receptors, ensuring vital interactions with the environment. Its functions are essential for maintaining homeostasis and overall bodily integrity.
4.2 Lab Exercises
Lab exercises for the integumentary system include histological examinations of skin layers and appendages. Students identify the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis under a microscope. Activities involve observing hair and nail samples, analyzing sweat and sebaceous gland functions, and exploring sensory receptors. Practical exercises, such as measuring sweat production and observing nail growth, provide hands-on insights. These exercises enhance understanding of the integumentary system’s structure and function, preparing students for clinical applications. Interactive discussions and self-assessment quizzes reinforce key concepts, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience.

Skeletal System
The skeletal system includes bones and joints, providing structural support and enabling movement. Labs focus on bone classification, joint types, and their functional roles in the body.
5.1 Bones and Joints
Bones and joints form the structural framework of the skeletal system. This section explores bone classification, including long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid bones, and their functions. Joints, or articulations, are examined to understand their types, such as synovial, cartilaginous, and fibrous joints, and their roles in movement. Lab activities include identifying bone markings, observing joint movements, and performing dissection exercises to visualize anatomical structures. Pre-lab and post-lab questions reinforce understanding of bone and joint anatomy and their physiological significance in the human body.
5.2 Nerves and Movement
This section focuses on the role of nerves in controlling voluntary and involuntary movements. It explores the structure and function of sensory and motor nerves, reflex arcs, and nerve plexuses. Lab exercises include nerve dissection, reflex testing, and observing nerve-muscle interactions. Activities emphasize understanding how nerves transmit signals and regulate movement. Pre-lab and post-lab questions help reinforce concepts, ensuring students grasp the intricate relationship between the nervous system and muscular function in coordinating body movements and maintaining physiological balance.
Muscular System
This section introduces the structure and function of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Lab exercises include muscle dissection, movement analysis, and identifying muscle groups using anatomical models.
6.1 Types of Muscles
This section explores the three primary types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and attached to bones, enabling movement. Smooth muscles are involuntary, found in internal organs, and facilitate functions like digestion. Cardiac muscle is specialized for the heart, ensuring rhythmic contractions. Lab exercises include identifying muscle types through dissection, studying histological slides, and analyzing their structural and functional differences using anatomical models and microscopes.
6.2 Muscle Movements and Exercises
This section focuses on understanding muscle movements and their underlying mechanisms. Students explore types of movements, such as flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, through hands-on activities. Lab exercises include observing muscle contractions under a microscope, analyzing movement patterns using anatomical models, and performing dissections to identify muscle attachments. Practical exercises emphasize the role of muscles in movement, enabling students to correlate structure with function and understand the physiology of muscle activity in various body regions.
Nervous System
This section introduces the structure and function of the nervous system, focusing on the central and peripheral nervous systems. Labs include dissections and microscopy to explore nerve tissues.
7.1 Central and Peripheral Nervous System
This section explores the structure and function of the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), comprising nerves and ganglia. Labs include dissections of neural tissues and microscopy to examine nerve structures. Activities emphasize understanding the roles of the CNS and PNS in controlling body functions and responding to stimuli. Pre-lab and post-lab questions reinforce key concepts, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of nervous system anatomy and physiology.
7.2 Reflexes and Sensory Responses
This section delves into the mechanisms of reflexes and sensory responses, exploring how the nervous system processes stimuli. Hands-on activities include nerve dissection, reflex testing, and simulations to demonstrate sensory pathways. Pre-lab and post-lab questions guide students in understanding the integration of sensory input and motor responses. The manual emphasizes the role of the nervous system in involuntary and voluntary actions, providing a detailed examination of reflex arcs and sensory receptor functions through interactive exercises and anatomical models.

Digestive System
This section explores the digestive system’s structure and function, from ingestion to excretion. Lab exercises include analyzing anatomical models and simulating digestive processes to understand nutrient absorption.
8.1 Anatomy of the Digestive Tract
The digestive tract, or alimentary canal, extends from the mouth to the anus, functioning in nutrient absorption and waste elimination. Key structures include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The mouth initiates digestion with teeth and enzymes, while the esophagus transports food via peristalsis. The stomach secretes digestive juices, breaking down food into chyme. The small intestine absorbs nutrients through villi, and the large intestine manages water absorption and waste formation. Lab exercises involve labeling diagrams, histological examinations, and simulations to explore these processes in detail.
8.2 Physiological Processes
The digestive tract’s physiological processes involve mechanical and chemical digestion, absorption, and waste elimination. In the mouth, saliva breaks down carbohydrates, while the stomach uses gastric juices to liquefy food. The small intestine absorbs nutrients via villi, facilitated by enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver. The large intestine absorbs water and forms feces. Lab exercises include analyzing enzyme activity, testing pH levels, and simulating digestion to understand these processes. These activities provide hands-on insights into how the digestive system maintains nutrient uptake and overall health.
Respiratory System
The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, enabling oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion. Lab exercises include lung dissection, spirometry, and histological examination of airway tissues to explore its functions.
9.1 Structure and Function
The respiratory system, essential for gas exchange, includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Its primary function is to facilitate oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion. The nasal cavity warms and humidifies air, while the alveoli in the lungs enable gas exchange. Lab exercises, such as spirometry and histological examinations of lung tissue, help students understand the structural and functional components of this system, emphasizing the importance of proper ventilation and gas exchange mechanisms in maintaining homeostasis.
9.2 Breathing Mechanisms
Breathing involves the coordinated action of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Inhalation occurs as the diaphragm descends, increasing chest cavity volume. Exhalation is passive, relying on elastic recoil. Lab exercises, such as spirometry, measure lung capacity and breathing rates. Histological slides of alveoli and bronchioles reveal microscopic structures essential for gas exchange. Students explore how accessory muscles enhance forced breathing, linking anatomical structures to physiological functions, and analyze factors affecting respiratory efficiency, such as posture and airway resistance, to understand the mechanics of breathing fully.
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, functioning to transport oxygen and nutrients. Lab exercises explore heart structure, vessel histology, and circulation mechanisms.
10.1 Heart and Blood Vessels
The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers: the right and left atria, and the right and left ventricles. Blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries, each with distinct structures and functions. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins return deoxygenated blood. Capillaries facilitate nutrient and gas exchange. Lab exercises involve histological examinations of blood vessel tissues and dissection activities to explore heart anatomy. These hands-on experiences help students understand the cardiovascular system’s role in circulation and overall bodily function.
10.2 Blood Circulation
Blood circulation is vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. The lab manual explores this process through activities such as tracing blood flow through the heart and blood vessels. Students examine histological slides of blood vessels to understand their structure and function. Interactive simulations and models are used to visualize blood movement and pressure dynamics. Post-lab questions reinforce understanding of how the cardiovascular system maintains homeostasis through efficient blood circulation.
Urinary System
The urinary system, comprising kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, filters waste and regulates fluid balance. Labs include kidney dissection and virtual simulations to explore its functions.
11.1 Kidneys and Urination
The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid balance. This section explores their structure, including the renal cortex and medulla, and their role in urine formation. Labs include dissection of kidney samples to examine nephrons and understand the process of filtration and reabsorption. Activities also cover the regulation of urination, emphasizing the role of the bladder and urethra. Interactive exercises and histological slides help students visualize the microscopic anatomy and physiological processes involved in waste removal and fluid conservation.
11.2 Fluid Balance Regulation
Fluid balance regulation is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, involving the kidneys, hormones, and electrolytes. Labs explore how the kidneys adjust blood volume and pressure by reabsorbing sodium and water. Activities include studying the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its role in fluid retention. Students analyze how antidiuretic hormone regulates water reabsorption and examine the impact of dehydration and overhydration on bodily functions. Interactive exercises and case studies help visualize the complex mechanisms ensuring proper fluid equilibrium and electrolyte balance, essential for cellular and organ function.

Reproductive System
This section explores the male and female reproductive systems, focusing on anatomical structures and physiological functions. Labs include dissections and activities to understand fertility, gamete formation, and hormonal regulation.
12.1 Male and Female Anatomy
This section provides a detailed exploration of the male and female reproductive systems, focusing on their unique anatomical structures and functions. Students examine the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, and the male reproductive organs, such as the testes, penis, and prostate gland. Labs include dissections, histological examinations, and activities to identify and understand the roles of these structures in reproduction. Pre-lab questions and vocabulary lists are provided to enhance learning and preparation.
12.2 Physiological Functions
This section delves into the physiological processes of the male and female reproductive systems, emphasizing gamete production, hormonal regulation, and reproductive cycles. Students explore the roles of estrogen, testosterone, and other hormones in maintaining reproductive health. Labs include activities to study fertilization, pregnancy, and parturition, as well as the physiological responses of reproductive organs. Interactive simulations and pre-lab questions help students understand the intricate mechanisms that govern human reproduction and its essential role in sustaining life.
Endocrine System
The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through hormones, produced by glands like the pancreas and thyroid. This section explores hormone production, regulation, and their roles in metabolism and growth.
13.1 Hormones and Glands
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, regulating various bodily functions. Key glands include the pancreas, thyroid, and adrenal glands, producing hormones like insulin, thyroxine, and adrenaline. These substances control metabolism, growth, and stress responses. Understanding hormone production and function is crucial for grasping endocrine system physiology. Lab exercises focus on identifying glandular structures and their roles in maintaining homeostasis. This section emphasizes the importance of hormone balance and its impact on overall health, highlighting disorders like diabetes and thyroid conditions.
13.2 Regulation of Metabolism
The endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating metabolism through hormones like insulin, glucagon, and thyroid hormones. Insulin lowers blood glucose, while glucagon raises it, maintaining energy balance. Thyroid hormones increase metabolic rate, influencing cellular energy production. Adrenaline accelerates metabolism during stress. Lab exercises explore hormone assays, blood sugar analysis, and case studies to understand metabolic disorders. These activities emphasize the integration of hormonal regulation in maintaining homeostasis and overall metabolic health, providing practical insights into endocrine system functions.
Lymphatic and Immune System
The lymphatic system aids in immune defense and fluid balance, while the immune system protects against pathogens. Labs explore lymphatic structures, immune cell identification, and response mechanisms.
14.1 Lymphatic Structures
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in immune defense and fluid balance. Key structures include lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, lymph vessels, and lymph fluid. Labs involve histological examinations of lymph nodes and spleen tissues to identify immune cells and understand their functions. Students also explore lymph vessel structure and lymph fluid composition. Hands-on activities include dissections and microscopy to visualize lymphatic components. These exercises enhance understanding of how the lymphatic system interacts with the immune system to protect the body and maintain overall health.
14.2 Immune Responses
The immune system protects the body against pathogens and diseases. Lab exercises focus on understanding innate and adaptive immunity, including cell-mediated and humoral responses. Students identify key immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages through microscopy. Activities include simulating phagocytosis and antibody-antigen interactions. Labs also explore the role of the spleen and lymph nodes in filtering pathogens and housing immune cells. These hands-on experiences help students grasp how the immune system detects, responds to, and neutralizes threats, maintaining overall health and preventing disease.
Dissection Exercises
Dissection exercises provide hands-on experience with anatomical structures. Labs include cat and fetal pig dissections, offering detailed exploration of organ systems and their functions.
15.1 Cat Dissection
The cat dissection exercise provides a detailed exploration of mammalian anatomy, with seven structured labs. Students examine external features, internal organs, and body systems, including skeletal and muscular structures. The dissection covers the thoracic and abdominal cavities, focusing on organ identification and their spatial relationships. This hands-on activity enhances understanding of anatomical terminology and functional connections, offering a comparative perspective to human anatomy. The exercise includes pre- and post-lab questions to reinforce learning and practical skills in dissection techniques.
15.2 Fetal Pig Dissection
The fetal pig dissection offers six detailed exercises, allowing students to explore mammalian anatomy and its relevance to human physiology. Labs focus on external and internal anatomy, including the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital systems. Students identify organs, tissues, and their spatial relationships, gaining insights into functional connections. Comparative analysis with human anatomy is emphasized, enhancing understanding of shared physiological principles. The exercises include pre- and post-lab questions, organ identification activities, and guided dissection protocols to ensure a comprehensive learning experience.
Review and Assessment
Post-lab questions and a comprehensive glossary reinforce learning, while interactive activities and assessments ensure mastery of anatomical and physiological concepts throughout the manual.
16.1 Post-Lab Questions
Post-lab questions are designed to reinforce understanding of key concepts and promote critical thinking. These questions cover lab activities, requiring students to apply knowledge gained during experiments. They include multiple-choice, short-answer, and essay-style queries, ensuring a comprehensive review of anatomical structures and physiological processes. The questions also encourage reflection on laboratory observations and data analysis. By completing these assessments, students can identify areas for further study and prepare effectively for exams. Regular review of post-lab questions enhances retention and deepens understanding of complex topics.
16.2 Glossary of Terms
The glossary of terms provides a comprehensive reference for key anatomical and physiological vocabulary encountered throughout the lab manual. Organized alphabetically, it includes definitions for complex terms, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding. This section serves as a quick reference for students to review and reinforce their knowledge of essential concepts. The glossary is particularly useful for preparing for exams, completing assignments, and engaging in class discussions. It also includes pronunciation guides and related terms, making it an invaluable resource for mastering the terminology of human anatomy and physiology.